Internet of Things
In the next few years the Internet of Things (IoT) will definitively transform business, as it will generate changes at a social and industrial level, its implementation will be total.
However, its application will also generate important changes in cybersecurity, which will have to be redefined, since incorporating a number of devices that in turn generate a large volume of data, increases to the same extent the vulnerability to cyberattacks.
There is talk of an exponential growth not only of Data but also of hardware and software for its control. This will imply higher levels of security, is the great challenge, IT professionals will have to assume new responsibilities to strengthen security policies, starting by designing new profiles and protocols for action on a larger scale and with a visible impact.
Ensuring the security of the Internet of Things (IoT) will be complex as they will have to be related to other approaches such as: cloud computing, mobile architectures, industrial control, automation and physical security. However, the basic principles of security will still be applicable.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is already present in many services, for example in Intelligent Power Networks, which control energy consumption in a locality or region, comparing home energy consumption and energy generation. To do this, smart meters are installed in homes to measure consumption.
This type of network, being vulnerable to cyberattacks, cybercriminals can make the electrical system collapse, as well as reduce or increase consumption costs. It can also happen in other critical structures such as a traffic control system, drug control system, among others.
The development of IoT is key to create intelligent cities, improve health, among other aspects of people’s daily lives. To the same extent it is essential to emphasize that safety recommendations in IoT systems to prevent cyberattacks in the future.
In the past, problems in public services were caused by system failures or natural disasters; now cyberattacks must be added. Learning from incidents, it is necessary to apply more secure policies and mechanisms for IoT Systems:
- Decrease the ease of use in order to increase the security of the system, encrypting data and communication.
- Do not rely on “read only”, since it is not secure, attackers always manage to meddle in systems, especially those developed in Linux because it is an operating system more susceptible to vulnerabilities than industrial systems, because it is more widespread.
- Any device is susceptible to cyber attack, it is essential to monitor the state of the system, including the nodes connected, in addition to take measures that detect failures in each of them.
- It is important to perform penetration tests, in an organized way following the security requirements of your system.
- Security is fundamental from the analysis, planning and design of the system. The IoT to be part of the social infrastructure, requires sufficient security measures.
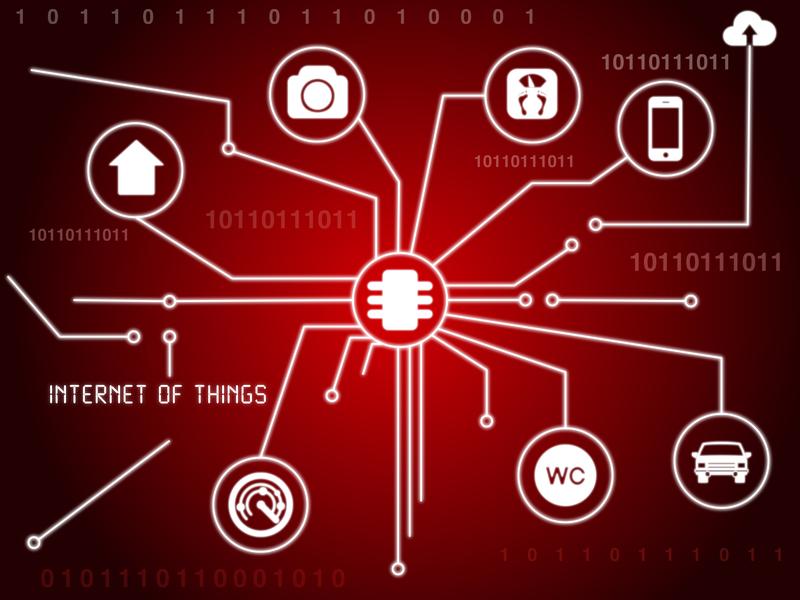
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
They are all technological devices that although they are in different areas, are connected, becoming intelligent devices, because through interconnection, they provide dynamic functionality to users, allowing them to exchange data, content updates, among others.
These devices range from connected vehicles, refrigerators, intelligent clocks, televisions, assistants, among many others that are manufactured daily.
Cybersecurity Risks in IoT Systems
There are many devices that at any given time put security or privacy at risk, because many manufacturers with the interest of offering their products to the market before the competition, devote little time and resources to audit the security of these devices and therefore do not guarantee the privacy of end users who incorporate them into their daily lives.
The truth is that cybersecurity problems continue to increase progressively, considering that the Internet was created to facilitate connectivity and in its design, development and implementation was not considered security so now requires redoubling efforts to achieve cybersecurity in the large Information Network, which will undoubtedly affect the Internet Systems of Things (IoT).
There are already many devices that are managed and incorporated into the personal and working lives of individuals, as well as organizations such as: Smart watch, Smart TV, refrigerator, Smart pone, among others.
It is therefore essential that professionals specialize in the cybersecurity sector to meet this demand for intelligent devices with proven security and thus contribute to the technological transformation is not overexposed to cyberattacks.
It is important to determine what should be protected and implement specific security measures for the protection of cyberattacks, is then required:
- Harmonize IoT security initiatives and regulations
- Make users aware of the importance of cybersecurity by defining security guidelines from the beginning of the hardware and software development lifecycle.
- Achieve interoperability in all systems to which intelligent devices are connected.
In the face of cybersecurity risks, it is necessary to examine the areas of attacks and threats, implement best practices and security recommendations to protect devices, data and the IoT system in general. To achieve this, the following aspects should be considered:
Incorporation of Devices into the IoT System: This is done through a series of automated steps supported by an application programming interface without human intervention.
To do so, it requires a trust anchor in the devices, which can be provided by the manufacturer or by the distributors or by the technological solutions team. This allows secure logging, deploying automated security controls.
Proprietary Controlled Safety: Despite the anchorage provided by the manufacturer, they are ideal for closed platforms or systems; when used in open systems they require user-controlled and application-specific safety.
IoT authentication: for devices enabled for IoT an authentication between devices and security management is required depending on the application, a combination of can be used: Application-specific credentials and trusted anchors.
Privacy and Data Integrity: The IoT are not just devices, it also involves data and to a large extent. This is a challenge for IoT, to control not only the large number of connected devices but to control the large volume of data they generate. For the protection of these data must be encrypted as close to the source, providing maximum security from end to end.
Secure Firmware Updates: Software and firmware updates for remote devices while ensuring the installation of trusted software is a security strategy applicable to the IoT. To be successful you must: authenticate secure devices, maintain data privacy and integrity on those devices.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a growing paradigm with significant technical, social and economic impact.
It presents new security and protection challenges that must be addressed in order to achieve the maximum potential to ensure the security of the products and services offered in the Internet System of Things (IoT) for the future.
The Internet of Things (IoT) brings us closer to that future, but its other side requires considering Cybersecurity Measures to prevent cyberattacks.